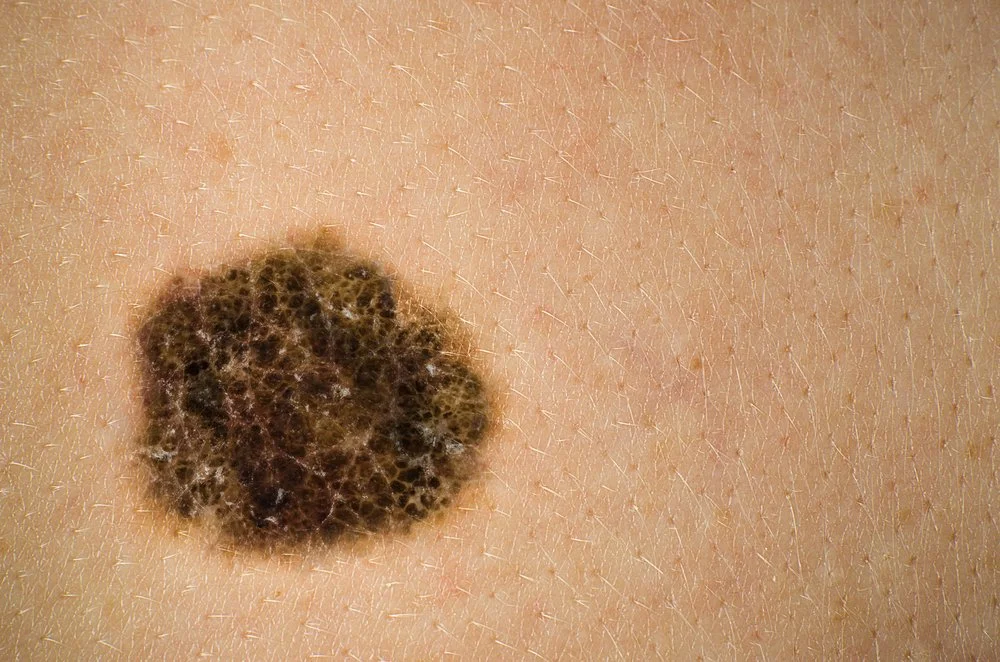
What's the relationship between melanoma and autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases and cancer are both complex conditions that impact one's health. While cancer and autoimmune diseases are distinct entities, research shows a growing body of evidence suggesting a link between the two. In a South Korean study, researchers found a significant association between melanoma and several autoimmune diseases. Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops in the cells that produce melanin, also known as melanocytes. These cells make the pigment that gives skin, hair, and eyes their color.
This research, published in The Journal of Dermatology, aimed to examine the relationship between melanoma and autoimmune diseases in Asian populations. Using multivariable logistic regression—a statistical technique that predicts the probability of an outcome based on multiple independent variables—on 12,040 patients with melanoma and 120,400 matched controls, researchers found that patients with melanoma had a significantly higher risk of developing autoimmune diseases.
They also discovered that the strongest association was observed with vitiligo, and that elevated risks were also seen for ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, ankylosing spondylitis, and type 1 diabetes. The researchers also looked at age and found that the association between melanoma and autoimmune diseases was more evident in patients aged 20 to 60 years compared to those older than 60.
This study highlights the possibility that genetic, environmental, and immunological factors contribute to the overlap between melanoma and autoimmune diseases. These findings could aid individuals diagnosed with melanoma by prompting them and their clinicians to monitor for early signs of autoimmune diseases. Further research on the link between skin cancer and other immune disorders needs to be conducted.
To support the Autoimmune Registry, please share our information with others who have autoimmune diseases. Donations are also greatly appreciated!